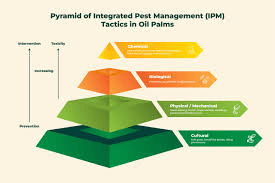
Integrated Pest Management (IPM) is a sustainable approach to pest control that focuses on preventing pest problems before they start, using a combination of biological, cultural, physical, and chemical methods. The goal of IPM is not to eradicate pests entirely, but to manage them in a way that minimizes risks to people, pets, and the environment. One of the key benefits of IPM is that it reduces reliance on chemical pesticides, which can be harmful if overused. Instead, IPM emphasizes a holistic approach to pest control by integrating various strategies that work together to keep pests at bay.
The first step in IPM is identifying the pest problem accurately. This includes understanding the type of pest, the source of the infestation, and its behavior. Once the pest has been identified, IPM focuses on preventing the pest from entering your home in the first place. This might involve modifying the environment, such as sealing cracks and crevices or removing sources of food and water. Biological controls, like introducing natural predators to target specific pests, can also be part of an IPM strategy. For example, using nematodes to control soil-dwelling pests or releasing ladybugs to combat aphids are both effective natural pest control methods that have minimal impact on the environment.
Physical and mechanical controls are also essential components of IPM. This includes setting traps, using barriers, or employing physical removal techniques. Chemical controls, such as targeted pesticides, are used only when necessary and are applied in a manner that minimizes exposure to non-target species. Because IPM uses a variety of methods, it is a more sustainable approach to pest control that reduces the need for harmful pesticides while still providing effective results. By using IPM, homeowners can protect their health, their homes, and the environment while keeping pests under control.